Testing Your Model Endpoints¶
In order to test your components you are able to send the requests directly using CURL/grpCURL or a similar utility, as well as by using our Python SeldonClient SDK.
Testing options¶
There are several options for testing your model before deploying it.
Running your model directly with the Python Client
Running your model as a Docker container
This can be used for all Language Wrappers (but not prepackaged inference servers)
Run your SeldonDeployment in a Kubernetes Dev client such as KIND
This can be used for any models
You can send requests through the generated Documentation UI, Python Client or CLI tools
Running your model directly with the Python Client¶
This can be used for Python Language Wrapped Models only
When you create your Python model, such as a file called MyModel.py with the contents:
class MyModel:
def __init__(self):
pass
def predict(*args, **kwargs):
return ["hello", "world"]
You are able to test your model by running the microservice CLI that is provided by the Python module
Once you install the Python seldon-core module you will be able to run the model above with the following command:
> seldon-core-microservice MyModel REST --service-type MODEL
2020-03-23 16:59:17,320 - seldon_core.microservice:main:190 - INFO: Starting microservice.py:main
2020-03-23 16:59:17,322 - seldon_core.microservice:main:246 - INFO: Parse JAEGER_EXTRA_TAGS []
2020-03-23 16:59:17,322 - seldon_core.microservice:main:257 - INFO: Annotations: {}
2020-03-23 16:59:17,322 - seldon_core.microservice:main:261 - INFO: Importing Model
hello world
2020-03-23 16:59:17,323 - seldon_core.microservice:main:325 - INFO: REST microservice running on port 5000
2020-03-23 16:59:17,323 - seldon_core.microservice:main:369 - INFO: Starting servers
* Serving Flask app "seldon_core.wrapper" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
2020-03-23 16:59:17,366 - werkzeug:_log:122 - INFO: * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Now that our model microservice is running, we can send a request using curl:
> curl -X POST \
> -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
> -d '{"data": { "ndarray": [[1,2,3,4]]}}' \
> http://localhost:5000/api/v1.0/predictions
{"data":{"names":[],"ndarray":["hello","world"]},"meta":{}}
We can see that the output of the model is returned through the API.
You can also send requests using the Python Client.
Running your model as a Docker container¶
If you are building language models with other wrappers, you are able to run the containers you build using S2I in your local docker client.
For this you just have to run the docker client with the following command:
docker run --rm --name mymodel -p 5000:5000 mymodel:0.1
This will run the model and export it on port 5000, so we can now send a request using CURL:
> curl -X POST \
> -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
> -d '{"data": { "ndarray": [[1,2,3,4]]}}' \
> http://localhost:5000/api/v1.0/predictions
{"data":{"names":[],"ndarray":["hello","world"]},"meta":{}}
You can also send requests using the Python Client.
Testing your model on Kubernetes¶
For Kubernetes you can set up a cluster as provided in the install section of the documentation.
However you can also run Seldon using local client providers such as KIND (we use KIND for our development and e2e tests).
Once you set up KIND or your kubernetes cluster of your choice, and you’ve set up your cluster with one of the supported Ingress (as outlined in installation docs), you can now send requests to your models.
Depending on whether you deployed Seldon Core with Ambassador or the API Gateway you can access your models as discussed below:
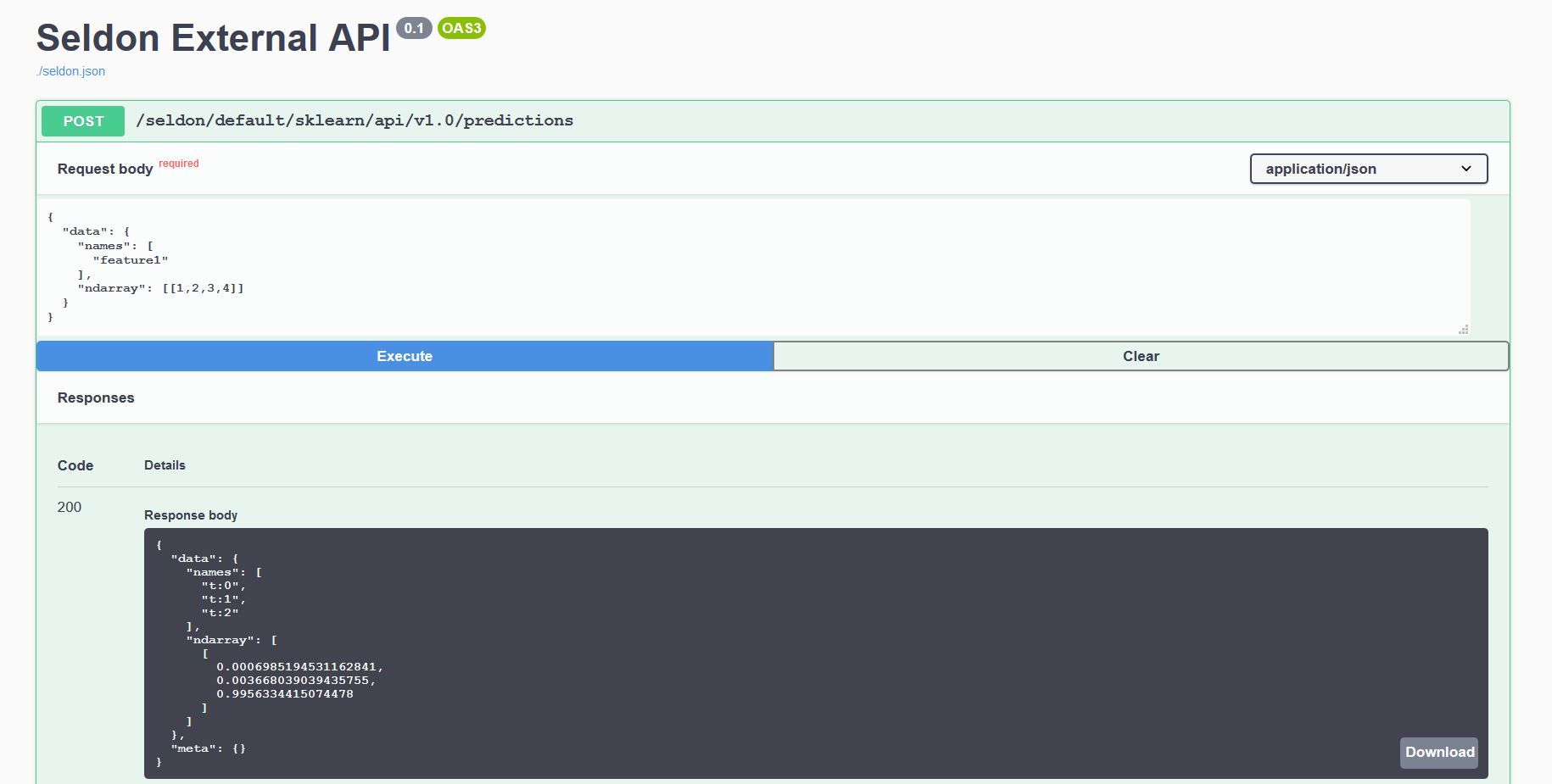
Generated Documentation Swagger UI¶
Every model deployed behind a Kubernetes cluster and an Ingress exposes a standardised User Interface to send requests using our OpenAPI schema.
This can be accessed through the endpoint http://<ingress_url>/seldon/<namespace>/<model-name>/api/v1.0/doc/ which will allow you to send requests directly through your browser.
Ambassador¶
Ambassador REST¶
Assuming Ambassador is exposed at <ambassadorEndpoint> and with a Seldon deployment name <deploymentName> in namespace <namespace>:
* A REST endpoint will be exposed at : ``http://<ambassadorEndpoint>/seldon/<namespace>/<deploymentName>/api/v1.0/predictions``
Ambassador gRPC¶
Assuming Ambassador is exposed at <ambassadorEndpoint> and with a Seldon deployment name <deploymentName>:
A gRPC endpoint will be exposed at
<ambassadorEndpoint>and you should send header metadata in your request with:key
seldonand value<deploymentName>.key
namespaceand value<namespace>.
Istio¶
Istio REST¶
Assuming the istio gateway is at <istioGateway> and with a Seldon deployment name <deploymentName> in namespace <namespace>:
A REST endpoint will be exposed at :
http://<istioGateway>/seldon/<namespace>/<deploymentName>/api/v1.0/predictions
Istio gRPC¶
Assuming the istio gateway is at <istioGateway> and with a Seldon deployment name <deploymentName> in namespace <namespace>:
A gRPC endpoint will be exposed at
<istioGateway>and you should send header metadata in your request with:key
seldonand value<deploymentName>.key
namespaceand value<namespace>.
Client Implementations¶
Curl Examples¶
Ambassador REST¶
Assuming a SeldonDeployment mymodel with Ambassador exposed on 0.0.0.0:8003:
curl -v 0.0.0.0:8003/seldon/mymodel/api/v1.0/predictions -d '{"data":{"names":["a","b"],"tensor":{"shape":[2,2],"values":[0,0,1,1]}}}' -H "Content-Type: application/json"
OpenAPI REST¶
Use Swagger to generate a client for you from the OpenAPI specifications.
gRPC¶
Use gRPC tools in your desired language from the proto buffer specifications.
Reference Python Client¶
Use our reference python client which is part of the seldon-core module.